| World Journal of Nephrology and Urology, ISSN 1927-1239 print, 1927-1247 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Nephrol Urol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjnu.org |
Case Report
Volume 2, Number 2, November 2013, pages 82-84
Cystic Lymphangioma of the Adrenal Gland: Case Report
Ebru Zemheria, Asif Yildirimb, Seyma Ozkanlia, c, Tulay Zenginkineta, Turhan Caskurlub
aDepartment of Pathology, Goztepe Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul Medeniyet University, Istanbul, Turkey
bDepartment of Urology, Goztepe Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul Medeniyet University, Istanbul, Turkey
cCorresponding author: Seyma Ozkanli, Tutuncu Mehmet Efendi Cad. Karanfil Sok., Ugur Apt. No: 16/3 Goztepe, Istanbul, Turkey
Manuscript accepted for publication October 11, 2013
Short title: Cystic Lymphangioma of the Adrenal Gland
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/wjnu114w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
In this case report, we present a case of a 27-year-old female who was evaluated for the left flank pain. Clinical and diagnostic work-up revealed a cystic mass at left suprarenal space. Surgical resection and histo-pathological findings were compatible with cystic lymphangioma of the adrenal gland. We discuss pathological differential diagnosis for cystic adrenal lymhangioma with a review of related literature on this unusual case.
Keywords: Adrenal gland; Adrenal cyst; Lymphangioma
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Benign malformations of vessels are called lymphagiomas that occur throughout the body with abdominal lesions and cystic lymphangiomas are large, well-circumscribed, multiloculated cystic spaces lined by endothelium containing a connective tissue component. In our case report, a 27-year-old female with left flank pain who underwent a clinical and diagnostic treatment that showed a cystic mass at left suprarenal space was presented. The pathological differential diagnosis for cystic adrenal lymphangioma and its compatibility with histo-pathological findings were also discussed.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 27-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital because of a left flank pain. On physical examination, she was normal. Abdominal ultrasonography (USG) revealed a 55 ´ 46 mm cystic mass without any septation or solid component located in the left adrenal space. A laboratory evaluation was done revealing unremarkable values for cortisol (28.12 µg/dL, normal range 5 - 25 µg/dL) and cortisol with 8 mg dexamethasone suppression test (0.35 µg/dL, normal < 3 µg/dL), 24-hour urinary metanephrine (115 µg, normal range 20 - 345 mg) and 24-hour urinary normetanephrine (42.5 µg, normal range 30-440 mg). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of adrenal glands (Fig. 1) was performed demonstrating the 60 mm contrast-enhanced cystic mass in the left adrenal gland.
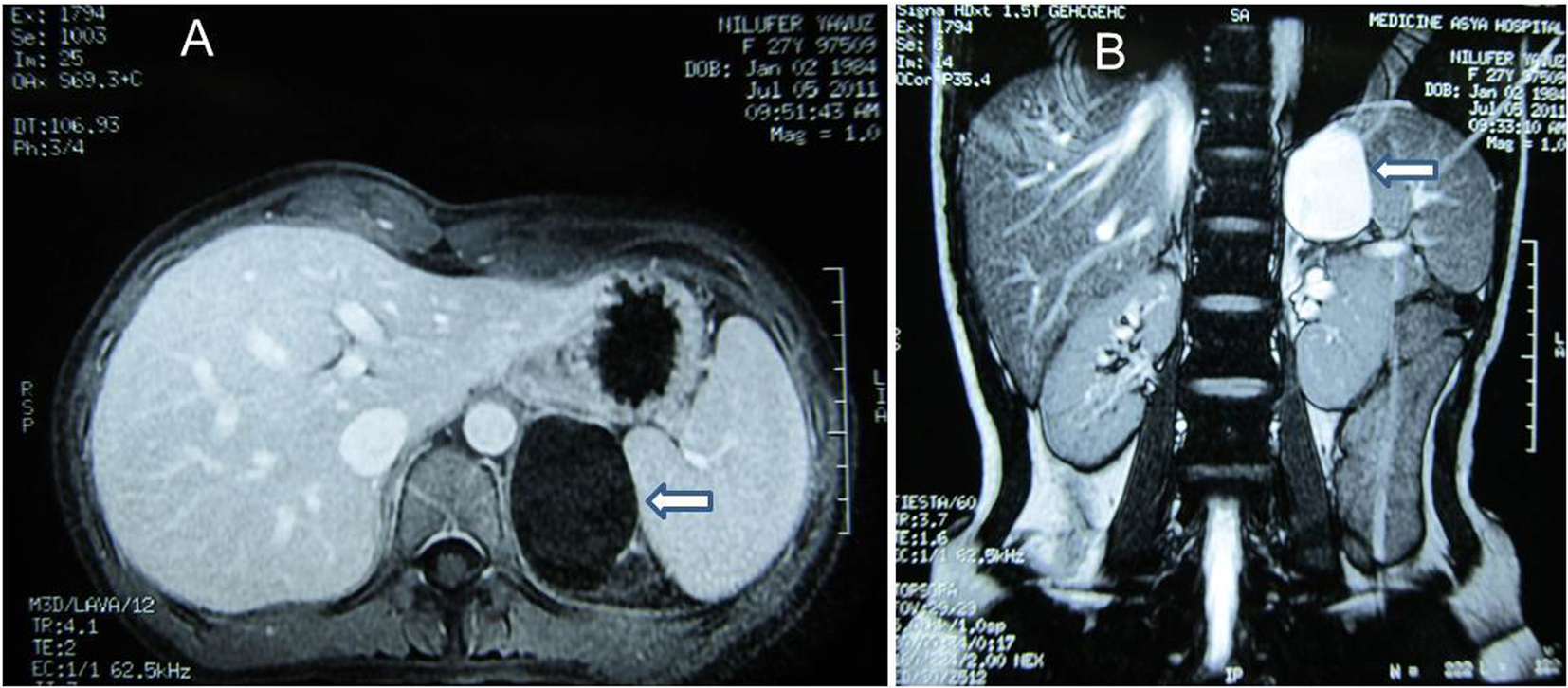 Click for large image | Figure 1. (A) MRI. Post-contrast axial T1-weighted image demonstrates cystic mass at left suprarenal location (arrow). (B) MRI. Post-contrast coronal breath hold T2-weighted image demonstrates cystic mass of 60 ´ 40 mm in diameter with homogenous high signal intensity (arrow). |
In April 2012, laparoscopic left adrenalectomy was performed for conclusive diagnosis. The patient was discharged from the hospital 2 days later with normal physical and laboratory findings. On pathological macroscopic examination, the adrenalectomy specimen weighted 32 g and measured 5 ´ 2.5 ´ 1 cm. Microscopic examination revealed multicystic architecture composed of irregular dilated spaces lined by flattened, bland, simple endothelial cells (Fig. 2). A significant endothelial atypia was not noted. Some of the cystic channels and spaces were detected acellular, homogeneous, proteinaceous material whereas red blood cells were not seen. Immunohistochemically, these cells stained positively for CD31 (Neomarker, clone JC/70A, 1:50 dilution; Freemont, CA, USA) and D2-40 (Neomarker, 1:50 dilution; Freemont, CA, USA) (Fig. 3). The cells were positive for smooth muscle actin (Neomarker, clone 1A4, same as asm1, 1:50 dilution; Freemont, CA, USA), which circumscribed the cyst. Histopathological diagnosis was cystic lymphangioma in the left adrenal gland.
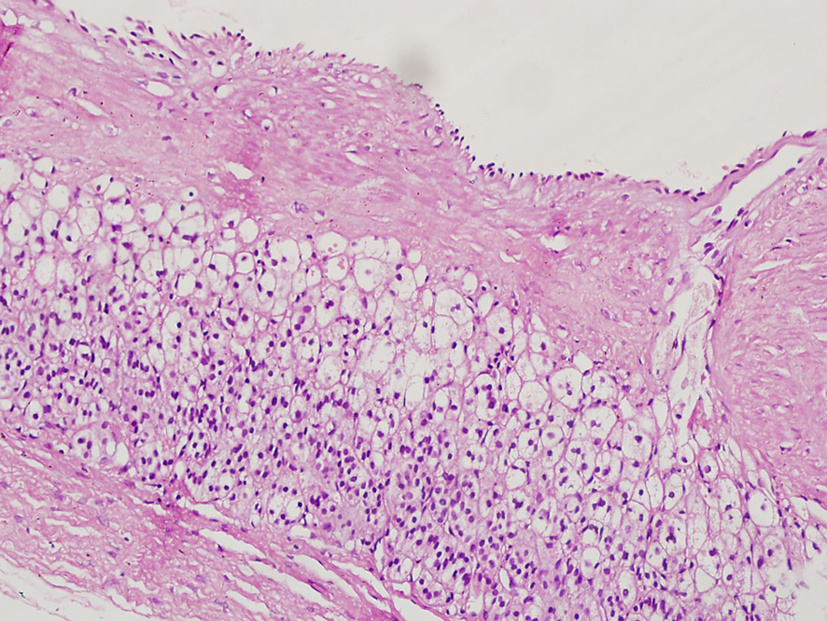 Click for large image | Figure 2. Histologically cystic lesion covered by flat endothelial cells adjacent to the normal-appearing adrenal gland. |
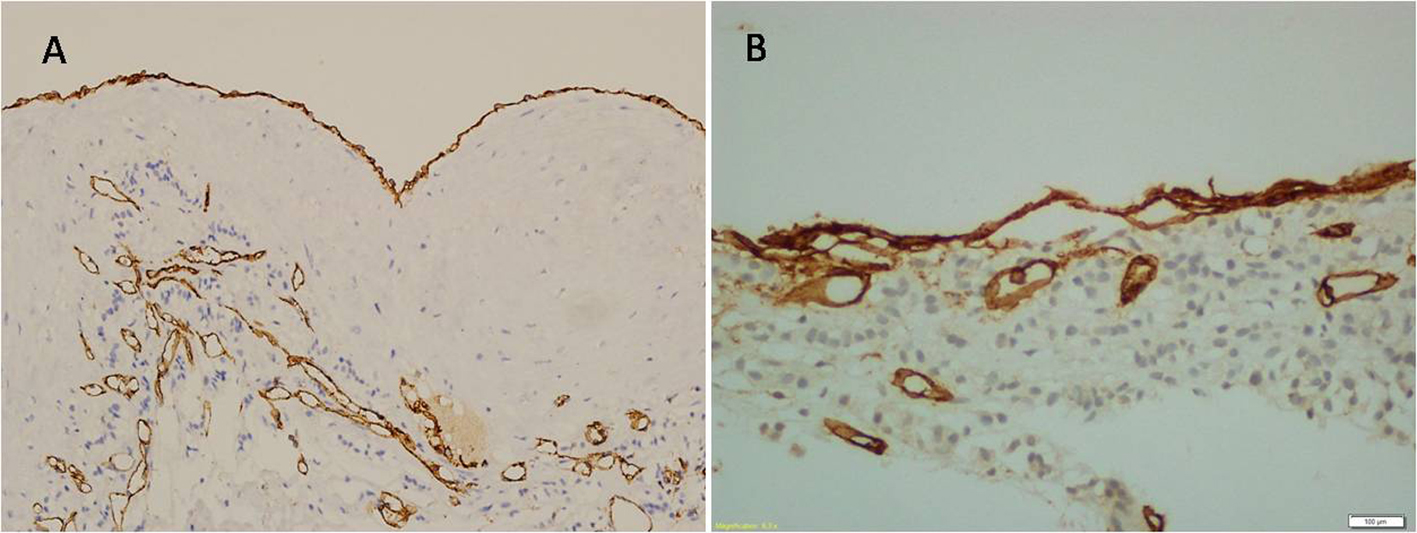 Click for large image | Figure 3. Flat endothelial cells are positive for D2-40 (A), and positive for CD31 (B). |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Cysts of the adrenal glands are very rare and most often identified incidentally during radiological investigation or at autopsy. Their incidence in autopsy studies has been reported in the literature to range from 0.064% to 0.18% [1, 2]. Adrenal cysts have been classified into four groups according to histological examination: endothelial cysts (45%), pseudocysts (39%), epithelial (9%), and parasitic cysts (7%) [3]. Endothelial cysts have identifiable endothelial cell lining, and the majority of them are lymphangiomatous. Pseudocysts generally occur after trauma, burns, shock, toxemia, and bleeding disorder in normal gland and adrenal tumor. Cystic adenomas, glandular or retention cysts, and cystic transformation of embryonic remnants are epithelial cysts. Parasitic cysts occur most commonly caused by echinococcal infection. Endothelial cysts are further subdivided into angiomatous and lymphangiomatous cysts [3, 4]. The endothelial cell lining reacts with Factor VIII-related antigen, CD31, and CD34 [5]. In addition, D2-40, a transmembrane mucoprotein, is expressed by lymphatic endothelial cells. Unlike other vascular markers (CD31 and CD34) labeling both blood vessel and lymphatic endothelium, D2-40 immunoreactivity is restricted to lymphatic endothelium. All over, lesions demonstrate a lack of cytokeration staining, further conforming to the lymphatic rather than mesothelial nature of lining cells [1].
In the presented case, the endothelial cell lining of cyst demonstrated positivity with both CD31 and D2-40.
Lymphangiomas are benign malformations of vessels, and occur throughout the body with abdominal lesions. Of all lesions, 95% are most commonly located in the neck, axillary region, and mediastinum, whereas remaining 5% are found in the abdominal cavity (intestine, omentum, mesocolon, or retroperitoneum). They are most frequently discovered between the third and sixth decades of life [6]. Lymphangiomas are subdivided into four histological categories: cystic, capillary, cavernous, and vasculolymphatic malformation [7]. These lesions are known as a variety of the same disease. Cystic lymphangiomas are large, well-circumscribed, multiloculated cystic spaces lined by endothelium that contain a significant connective tissue component.
Although the pathogenesis of lymphangioma is not completely resolved, the most reasonable theory is that lymphangioma arises from abnormal development and/or dilation of lymphatic vessels [8]. However, alternative theory is that lymphangioma lesions result from blockage of proximal lymphatics or trauma [1].
Adrenal cystic lymphangiomas are usually asymptomatic. Symptoms such as pain, gastrointestinal disturbance, or a palpable mass can occur due to the size and position of the cyst [3]. Laboratory findings are usually nonspecific, whereas rarely small adrenal cysts may be associated with Cushing syndrome, virilization, or pheochromocytoma. Ellis et al reported a total of nine adrenal lymphangiomas (six women and three men) between 1984 and 2008 at the Johns Hopkins Hospital [1]. All nine patients were adult at the time of diagnosis with a mean age of 42 years (range, 28 - 56 years). They detected all lesions during a work-up for abdominal pain or incidentally as a large-size mass.
Clinical management of cystic adrenal lymphangioma can be decided by the imaging and laboratory findings. If the suspicion of malignancy is low, some authors recommend aspiration of the adrenal cyst for diagnosis and management rather than surgical excision [9]. This management has a limited diagnostic ability to determine histology and the high incidence of reaccumulation of cyst fluid [5]. Surgery is indicated for large, complicated, functional, and symptomatic adrenal cysts.
Conflict of Interest and Funding
We, as the authors of this manuscript, declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article and that we do not have a direct financial or personal relation with any people or organizations. We certify that we have participated sufficiently in the intellectual content, the analysis of data. Each of us has reviewed the final version of the manuscript and approves it for publication. Should the editors request the data upon which the work is based, the authors shall produce it.
| References | ▴Top |
- Ellis CL, Banerjee P, Carney E, Sharma R, Netto GJ. Adrenal lymphangioma: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical characteristics of a rare lesion. Hum Pathol. 2011;42(7):1013-1018.
doi pubmed - Bellantone R, Ferrante A, Raffaelli M, Boscherini M, Lombardi CP, Crucitti F. Adrenal cystic lesions: report of 12 surgically treated cases and review of the literature. J Endocrinol Invest. 1998;21(2):109-114.
pubmed - Longo JM, Jafri SZ, Bis KB. Adrenal lymphangioma: a case report. Clin Imaging. 2000;24(2):104-106.
doi - Ates LE, Kapran Y, Erbil Y, Barbaros U, Dizdaroglu F. Cystic lymphangioma of the right adrenal gland. Pathol Oncol Res. 2005;11(4):242-244.
doi pubmed - Tagge DU, Baron PL. Giant adrenal cyst: management and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1997;63(8):744-746.
pubmed - Garcia M, Louis LBt, Vernon S. Cystic adrenal lymphangioma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004;128(6):713-714.
pubmed - Fauquenot-Nollen AM, Plaisier ML, Tjon ATRT. Combined thoracic and abdominal lymphangioma in an adult. JBR-BTR. 2002;85(3):130-131.
pubmed - Erickson LA, Lloyd RV, Hartman R, Thompson G. Cystic adrenal neoplasms. Cancer. 2004;101(7):1537-1544.
doi pubmed - Gleeson MJ, McMullin JP. Cystic lymphangiomata of the adrenal gland. Br J Urol. 1988;62(1):93-94.
doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
World Journal of Nephrology and Urology is published by Elmer Press Inc.