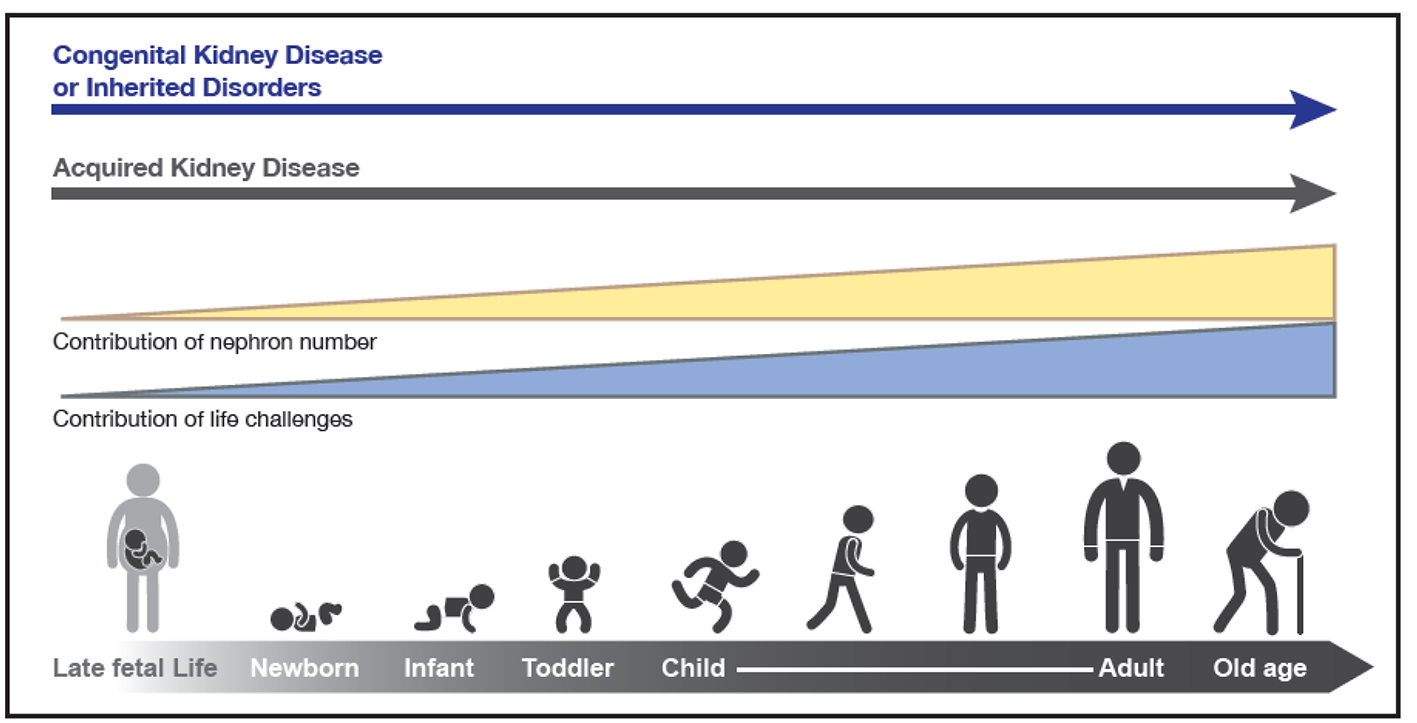
Figure 1. The types and risks of kidney disease change across the lifecycle. The contribution of nephron number increases over the life cycle, in concert with events that provide direct insults and challenges to kidney health.
| World Journal of Nephrology and Urology, ISSN 1927-1239 print, 1927-1247 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Nephrol Urol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjnu.org |
Editorial
Volume 000, Number 000, January 2016, pages 27-32
Averting the Legacy of Kidney Disease: Focus on Childhood
Figure

Tables
| The data in this table are as defined by the World Health Organization. The perinatal period is defined as 22 completed weeks of gestation to day 7 of life; the neonatal period, as up to 28 days of life; infancy as up to 1 year of age; childhood as years 1 - 10; and adolescence from 10 years to age 19. There is variation worldwide in how these stages of early life are defined. Some would define “young people” as those aged 24 or less. In the United States, childhood is as a whole defined as going to age 21. | |
| Perinatal period | 22 completed weeks of gestation to day 7 of postnatal life |
| Neonatal period | Birth to day 28 of postnatal life |
| Infancy | Birth to 1 year of age |
| Childhood | 1 year of age to 10 years of age |
| Adolescence | 10 years of age to 19 years of age |
| Etiology | CKD, percentage (range) | ESRD, percentage (range) |
|---|---|---|
| Rare causes include congenital NS, metabolic diseases, and cystinosis. Miscellaneous causes depend on how such entities are classified. CAKUT: congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract; GN: glomerulonephritis; HN: hereditary nephropathy; HUS: hemolytic uremic syndrome. *From Harambat et al. CKD data are from NAPRTCS, the Italian Registry and the Belgian Registry. ESRD data are from ANZDATA, ESPN/ERA-EDTA, UK Renal Registry and the Japanese Registry. | ||
| CAKUT | 48-59% | 34-43% |
| GN | 5-14% | 15-29% |
| HN | 10-19% | 12-22% |
| HUS | 2-6% | 2-6% |
| Cystic | 5-9% | 6-12% |
| Ischemic | 2-4% | 2% |